eBook
Unlocking innovation in Aerospace and Defense
Shorten aircraft design cycles with ESTECO’s digital engineering solutions for collaboration, simulation data management and multidisciplinary design optimization.
Webinar
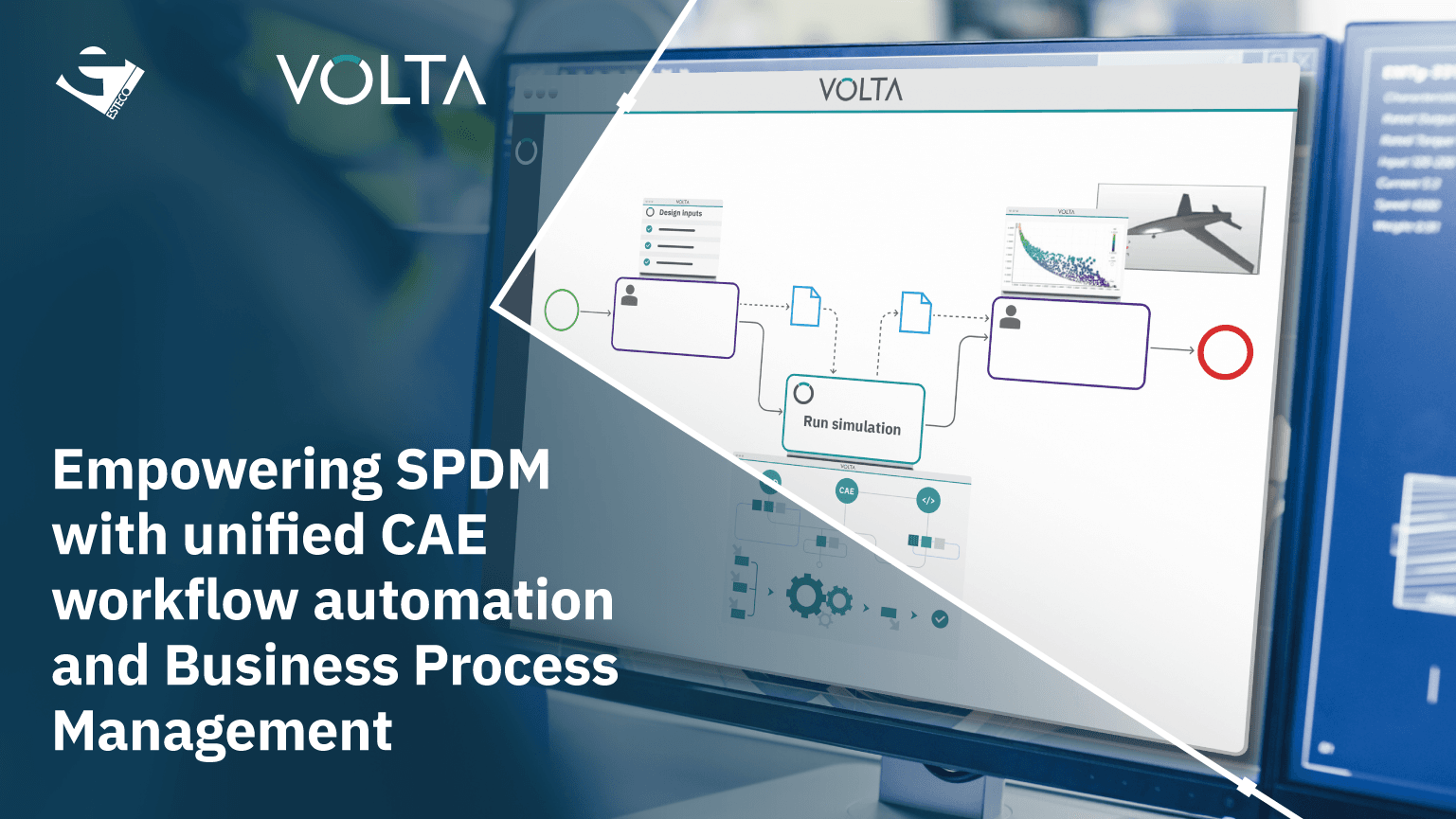
Empowering SPDM with unified CAE workflow automation and Business Process Management
Take a 30-minute deep dive into VOLTA BPM technology and learn how to automate human interactions and integrate simulation execution in a business process workflow.
Search results
Showing 31 - 40 of 43 results
Webinar
Shroud Design Exploration using PowerFLOW integrated with modeFRONTIER
This webinar, cohosted by ESTECO and EXA Corporation in 2017, presents the successful integration of PowerFLOW simulation technology in the modeFRONTIER workflow to provide Ditch Witch® with valuable insight to guide the shroud design on one of its Vacuum Excavators.
Watch it to find out how Ditch Witch® have performed multiple analyses, by integrating EXA's PowerFLOW simulation technology into modeFRONTIER workflow, on their equipment to gain a deep understanding of how key design parameters impact performance and manufacturing costs – critical inputs for next-generation machine designs.
AGENDA
Overview of EXA and ESTECO
Focus on Simulation Driven Design Exploration > how to exploit PowerFLOW simulation software into modeFRONTIER workflow
Case study > Explore shroud design options to improve machine performance of a FX65 Vacuum Excavator
Webinar
Reliability based robust design optimization of a free-fall-life-boat
This webinar, hosted by ESTECO and BETA CAE Systems, focuses on a reliability-based optimization method that statistically increases the safety of free fall lifeboats, which are typically used to evacuate passengers in oil platforms and large transport vessels.
Dimitris Drougkas from BETA CAE Systems and Alberto Clarich from ESTECO demonstrate the advantages of the integration of their software in the modeFRONTIER multi-objective design environment for a reliability based optimization of a free fall lifeboat.
ANSA software is used to morph the free fall lifeboats mesh by editing its shape and its initial position, and modeFRONTIER is used to automate the simulations performing an optimization under the uncertainties of the operational parameters.
Success story
modeFRONTIER helps Azimut Benetti optimize yacht propeller performance
Using modeFRONTIER to perform multi-objective cavitating propeller optimization
Azimut Benetti Group is the world’s largest network producing megayachts and leading private group in the luxury yacht industry. Azimut-Benetti’s R&D Centre develops unique technologies, for an effortless and safe navigating experience. The Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering Unit (DITEN Department) of Genoa University work jointly with DETRA Custom Propellers and Azimut Benetti’s R&D Centre, using modeFRONTIER to optimize the design of a custom propeller for a high- speed Azimut Benetti 95 RPH yacht. ## Challenge
The design of a propeller is always a trade-off between competing objectives and constraints: maximizing the propulsion efficiency and ship speed while avoiding cavitation and maintaining a sufficient blade strength. The traditional lifting line / surface methodologies define the propeller shape by including simplified geometric assumptions that make them not suitable for modern fast propellers design. The application of more accurate flow solvers and the automatic investigation, possible through the parametric description of the geometry (unconventional combinations of pitch, camber, or, for instance, local hydrofoil shapes), proves to be a successful design alternative for a high-speed propeller. ## Solution
Following this new approach, the optimization of a reference propeller with modified rake distribution was driven by the MOGA-II, the genetic algorithm included in the automation workflow in modeFRONTIER. The experimental data collected at the cavitation tunnel confirmed the reliability of both the Boundary Elements Method and RANSE numerical approaches.
A dedicated full-scale sea trials, performed with propellers manufactured by Detra, showed that the cruise speed achieved with the optimized propeller is 1 kn higher than the baseline propeller speed, geometry by while the cavitating behavior was also significantly enhanced. “The result is remarkable, especially keeping in mind that the increase of cruise speed, together with the enhancement of comfort onboard, is crucial to the perception of luxury yacht customers”, said Francesco Serra, R&D Office, Azimut Benetti Group. ## Benefits
modeFRONTIER helped build an optimization framework to interact with the parametric description of the geometry to define each new blade shape and employ flow solvers to quantify how each propeller fulfills the constraints and the objectives of the design. “Starting from a set of 48 blade parameters to alter the reference propeller geometry, the use of MOGA-II algorithm allowed to compute and test 50,000 different geometries in about 5 days to achieve a satisfactory Pareto convergence and choose optimal candidates (one for any rake distribution) for RANSE analyses” said Michele Viviani, Associated Professor at DITEN Department, Genoa University.
Webinar
A CAD-Mesh mixed approach to enhance shape optimization capabilities
In this joint webinar, ESTECO and RBF Morph present an innovative CAD-Mesh mixed approach to enhance shape optimization capabilities.
Riccardo Cenni from SACMI describes how engineers at SACMI Ceramic Engineering Department leveraged modeFRONTIER, RBF Morph and ANSYS Workbench to develop an hybrid methodology combining CAD and mesh based approach overtaking the limits of the shape optimization based on the single disciplines. The approach helped find better solutions for the SACMI industrial component analyzed and turns out to be promising for future optimization projects.
Agenda:
Overview on ESTECO and its technology
Overview on RBF Morph and its technology
Introduction to SACMI and the engineering challenge
Shape optimization: the CAD-based, the Mesh-based and the mixed approach
Optimization results and takeaways
Webinar
Integrating XFlow, WB-Sails and modeFRONTIER for olympic sail optimization
In this joint webinar, expert engineers from WB-Sails, Next Limit Dynamics and ESTECO demonstrate the advantages of the integration of their software, illustrating the details of the models, and presenting the results of the optimization.
The focus of the webinar is to illustrate the optimization process used to enhance the shape of the sails used for Olympic disciplines and produced by the Finnish WB-Sails.
The “flying shape” of the sail is modeled by a parametric CAD (Catia v5), and a non-stationary simulation is performed using XFlow, the CFD software by Next Limit Dynamics, recently acquired by Dassault Systèmes. The automatic simulation process was set up in modeFRONTIER. With only few simulation the optimization algorithm was able to identify the optimal shape, while minimizing resistance and heeling moment on the boat.
Agenda:
Olympic Sail Parametrization (Catia v5)
modeFRONTIER integration with XFlow CFD software
Optimization results and post-processing analysis
Webinar
Integrating modeFRONTIER with Enventive and ANSYS Workbench
ESTECO and Enventive Engineering Inc. present the integration of modeFRONTIER, Enventive®, and Ansys Workbench to optimize the shape of an electrical connector.
In this webinar Alexander Duggan ( Senior Application Engineer, ESTECO) and Kristin Dawson (Product Manager, Enventive Engineering, Inc.) demonstrate using Enventive® to analyze variation of the forces and friction between a pin and connector, coupled with using Ansys Workbench to determine the stress in the connector as it is deflected by the pin. By integrating Enventive® and Ansys Workbench, modeFRONTIER can optimize design parameters to ensure that the pin insertion force and contact reaction force fulfill design requirements while ensuring that the stress in the connector component does not exceed the yield strength of the material.
Agenda:
ANSYS Workbench for finite element analysis (FEA)
Enventive's force and dimentional variation analysis
modeFRONTIER integration with Enventive and ANSYS Workbench
Webinar
Complex Workflow Management with modeFRONTIER 2016
In this webinar Alberto Clarich (Technical Manager, ESTECO) and Giulio Cassio (Application Engineer, ESTECO) demonstrate how modeFRONTIER provides new advanced features for project complexity handling: a dedicated panel for workflow setting (Workflow Global Properties), the Design Space Node, the improved Subprocess Node and many more.
Watch it and learn how:
Automate the execution of complex chains of preprocessing and simulation tools with modeFRONTIER.
Take advantage of the very flexible workflow and the wide range of direct integration nodes for the most popular simulation tools.
Optimize your design choosing among of innovative algorithms to determine the set of best possible solutions combining the complex set of opposing objectives.
Webinar
Make your design optimization project run fast with modeFRONTIER and ANSYS HPC Parametric Pack
This webinar, cohosted by ESTECO and Ansys, demonstrates the benefits of using the new integration between Ansys HPC Parametric Pack and modeFRONTIER 2016 by presenting the results of two industrial application in the automotive field.
Why watching this webinar?
This webinar give insights on how to better leverage company's private cloud or HPC systems for faster simulation analysis.
The case studies will show how to make the use of computational resources more efficient and save time with the joint use of the newly released modeFRONTER 2016 and ANSYS WB HPC Parametric Pack, that will make design optimization projects execute faster.
The first application was developed by BorgWarner Morse system and EnginSoft, dealing with the optimization of a tensioner arm.
The second case study is aimed at improving the design of heat exchangers and part of an EU funded project, OptimHex.
Webinar
Spot on Response Surface Methods (RSM) in modeFRONTIER
In this webinar, Danilo Di Stefano (Product Manager at ESTECO) and Alberto Clarich (Technical Manager at ESTECO) demonstrate the newly added RSM Trainer Node, and how to combine it with the innovative Adaptive Space Filler (ASF) and other analytics tools in modeFRONTIER.
RSM-based optimization is an excellent strategy to manage heavy simulation processes: by acting as surrogates of simulation models, RSMs let engineers fast-run the classic optimization process.
Why watching this webinar?
This webinar give insights on the advanced RSM capabilities included in modeFRONTIER
Discover the new automation of RSM training and learn how to re-use the model both for the same workflow and other projects
Find out how the new Adaptive Space Filler combines state-of-the-art space filling strategies with the predictive ability of response surfaces.
Get to know two real-world case studies leveraging modeFRONTIER RSM capabilities
Success story
Petrobras Designs the P-55 platform using modeFRONTIER
How ESTECO’s first Brazilian customer optimized the largest semi-submersible platform in the country
Last year Petrobras, a state-owned publicly traded Brazilian multinational energy corporation headquartered in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, launched their P-55 offshore platform, which was initially sized using modeFRONTIER. In order to tackle the complex problem of multiple variables, constraints and objectives, as well as a desire for a rational approach to the design process, Petrobras turned to modeFRONTIER to help them with the optimization study. ## Challenge
Defining the main dimensions of an offshore production platform is a complex problem due to the many variables that can influence the behavior of the platform, including: deck area, deck weight, subsea systems interface, stability issues and wave-induced motions. The dimensioning process is affected by many constraints imposed by more stringent motion requirements, construction and assembly considerations, as well as by the draft limit of shipyards. Ultimately the goal is to reduce to a minimum the vertical wave-induced motions which can cause fatigue damage to the steel catenary risers (the pipes which bring the oil from the seabed to the platform) ## Solution
Dr. Mauro Costa de Oliveira, a naval architect at CENPES, the Petrobras Research Center in Rio, and the first user of modeFRONTIER in Brazil, used the software to integrate the hydrodynamics analysis tool, WAMIT, and CENPES’s own stability software, SSTAB. He then went on to run an optimization study in which modeFRONTIER varied 5 key geometric parameters of the platform with the objective of minimizing, subject to numerous constraints, vertical motion of the platform due to wave loading. During the study, the structure was analyzed for multiple conditions: quayside, transit and in operation with 2 different wave load conditions. Using one of modeFRONTIER’s genetic algorithms to drive the search process, Dr Costa de Oliveira was able to identify the designs which met all the constraints, and from among those to select the configuration with the lowest riser vertical motion. The feasible region (ie the part of design space where all constraints were respected) is very small - to identify this region without the help of a tool like modeFRONTIER would have been almost impossible. The final design is shown in Fig. 2. ## Benefits
“modeFRONTIER - Dr Costa de Oliveira says - proved to be invaluable in helping us to address the complex problem of selecting the main dimensions of a deep water floating production system, where there is potentially a huge number of alternatives to be evaluated. The software allowed us to rationalize our approach to the problem and conduct an automatic search, driven by a genetic algorithm, which quickly identified the best design which met all constraints. The post-processing tools also proved to be extremely useful for the conceptual phases of the design of a deep water floating production system”. In January 2014 the P-55 began operation in Brazil’s Roncador field at a site where the depth of the seabed is 1,800 meters. At 52,000 tons and 10,000 square meters in size and displacing 105,000 tons, the P-55 is the largest semi-submersible platform built in Brazil and one of the largest of its kind in the world; it is capable of processing 180,000 barrels of oil per day , compressing 6 million cubic meters of natural gas per day, and injecting 290,000 barrels of water per day.